- +1-707-722-7066
- care@flashtestbio.com
English
FLASHTEST is more than just a manufacturer; we're a partner in your diagnostic success. We recognize that each market has unique requirements, which is why we offer comprehensive customization services. From original design and development (ODM) and efficient manufacturing (OEM) to full technology transfer and production setup, we provide the expertise and support you need. Our core strengths lie in molecular diagnostics, immunology, and lab automation, with a strong focus on PCR and immunofluorescence technologies. We're committed to building long-term partnerships with our international clients. Contact us to explore how we can work together.
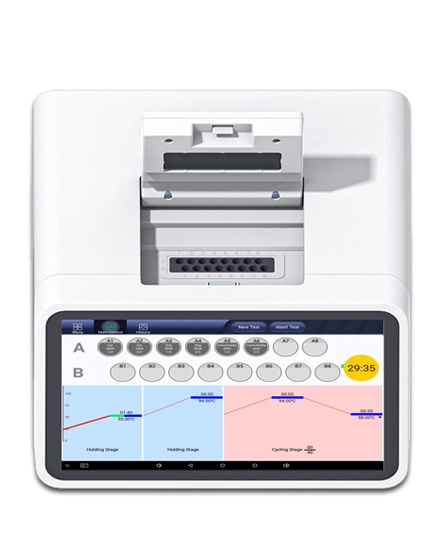
Denaturation: The PCR instrument initially heats the DNA sample to a high temperature, typically around 95°C, which causes the double-stranded DNA to separate or denature into two single strands.

Annealing: After denaturation, the temperature is lowered to around 50-65°C, allowing primers (short DNA sequences) to bind or anneal to their complementary sequences on each single DNA strand. The primers serve as starting points for DNA replication.

Extension: The temperature is raised to around 72°C, and a DNA polymerase enzyme is added to the reaction mixture. The enzyme extends the primers by adding complementary nucleotides to each single DNA strand. This process results in the synthesis of new DNA strands that are complementary to the original template strands.

These three steps (denaturation, annealing, and extension) constitute one cycle. PCR instruments can run multiple cycles, typically ranging from 20 to 40 cycles, amplifying the specific DNA target exponentially with each cycle.By controlling the temperature precisely and cycling through these steps rapidly, PCR instruments facilitate the amplification of even a small amount of DNA or RNA into millions to billions of copies, enabling various applications such as genetic testing, diagnostics, genotyping, cloning, and DNA sequencing.

1. Quantitative Analysis: Real-Time PCR instruments allow for the accurate and precise quantification of DNA or RNA targets, providing information about the initial amount of target molecules present in the sample.
2. Rapid Results: Real-Time PCR provides faster results compared to traditional PCR methods. The data is generated in real-time during the amplification process, eliminating the need for post-amplification analysis.
3. High Sensitivity: Real-Time PCR instruments can detect very low levels of nucleic acid targets, making them highly sensitive tools for detecting even small amounts of pathogens or genetic material.
4. Multiplexing Capability: These instruments have the ability to detect and quantify multiple targets simultaneously in a single reaction, saving time and resources.
5. Wide Range of Applications: Real-Time PCR is utilized in various fields such as research, clinical diagnostics, food safety, environmental testing, and genetic analysis. Its versatility makes it a valuable tool in many disciplines.

There are several reasons why a real-time PCR instrument is needed:
A real-time PCR instrument is needed for its ability to accurately and quickly detect and measure specific genetic material. It provides high sensitivity and specificity, allowing for early detection of diseases or genetic mutations. The instrument has a wide range of applications in medical diagnostics, research, and forensic analysis. It offers the advantage of rapid and precise results, high throughput capability, and standardized protocols, ensuring reproducibility. Overall, a real-time PCR instrument is essential for efficient and accurate genetic analysis in various fields.

PCR instruments play a crucial role in several applications:
1. Research: PCR instruments are extensively used in molecular biology research for amplifying and studying specific DNA or RNA sequences. They enable researchers to investigate gene expression, identify genetic variants, analyze DNA fragments, and study the functions of specific genes.
2. Diagnostics: PCR instruments are used in clinical diagnostics, veterinary medicine, and pathogen detection. They can detect the presence of infectious agents, genetic mutations, or disease markers in patient samples, aiding in the diagnosis and monitoring of diseases.
3. Forensics: PCR instruments play a significant role in DNA profiling and forensic analysis. They allow forensic scientists to amplify and analyze DNA samples from crime scenes, identify suspects, establish familial relationships, and provide evidence in legal investigations.
4. Quality control: PCR instruments are utilized in various industries, such as food safety, agriculture, and environmental testing, for quality control purposes. They can detect the presence of contaminants, pathogens, or genetically modified organisms.
Get In Touch With Us Now!
Tel:
+1-707-722-7066Email:
care@flashtestbio.comAdd:
Blk A4 - F2, Liyuan Development Zone, Binhu District, Wuxi, China